This code is for a 12f683 pic, connected to TIP31 transistors and white LEDs. It generates a variety of strobe effects. Randomly it will create either darkness (none), synchronized strobe on both channels, random strobe on both channels, the duration of the on pulse and off pulse also varies randomly. This makes a great Halloween effect.
/*
* File: strobemain.c
* Author: hmikelson
*
* Created October 2016
*/
#if defined(__XC)
#include <xc.h> /* XC8 General Include File */
#elif defined(HI_TECH_C)
#include <htc.h> /* HiTech General Include File */
#endif
#include <stdint.h> /* For uint8_t definition */
#include <stdbool.h> /* For true/false definition */
#include <stdlib.h> /*rand()*/
#pragma config MCLRE=OFF,CP=OFF,WDTE=OFF,FOSC=INTOSCIO
#define _XTAL_FREQ 4000000
uint8_t sGPIO;
void init()
{
//Configure GPIO Port
ANSEL = 0b00000000; //Configure all GPIO pins as digital
TRISIO = 0b11001000; //Set GP3 as input and the rest as outputs
// GP0 = eye 1, GP2 = eye 2, GP5 = speaker, GP4 = piezo
OPTION_REGbits.nGPPU = 0;
WPU = 0b00000100; //Enable weak pullups on GP2
//Configuer AD Convertor
ADCON0 = 0x00; //AD disabled
ADRESH = 0x00; //Init the AD Register
//Configure Comparator
CMCON0 = 0xFF; // Comparator is turned off
CMCON1 = 0x00; // Comparator is turned off
//Interrupt configuration
INTCON = 0x00; //Disable all interrupts
}
void vdelay(int n)
{
int i;
for (i=0;i<=n;i++)
{
__delay_us(1);
}
}
void strobe1(int r)
{
int i,n;
n=200/r;
for (i=0;i<n;i++)
{
GPIO = 0b11000011;
vdelay(100);
GPIO = 0b11000000;
vdelay(r*1000);
}
}
void strobe2(int r)
{
int i,n;
n=200/r;
for (i=0;i<n;i++)
{
GPIO = 0b11000011;
vdelay(200);
GPIO = 0b11000000;
vdelay(r*1000);
}
}
void strobe3(int r)
{
int i,n,r1;
n=200/r;
for (i=0;i<n;i++)
{
r1 = rand()%16;
GPIO = 0b11000011;
vdelay(100);
GPIO = 0b11000000;
vdelay(r1*1000);
}
}
void strobe4(int r)
{
int i,n,r1;
n=200/r;
for (i=0;i<n;i++)
{
r1 = rand()%16;
GPIO = rand();
vdelay(100);
GPIO = 0b11000000;
vdelay(r1*500);
}
}
void darkness(void) // PWM sweep high f to low f
{
GPIO = 0b11000000;
__delay_ms(2000);
}
void main()
{
uint8_t r,r2;
init();
while(1)
{
r=rand()%8;
//r=2;
r2 = rand()%32+1;
switch (r)
{
case 1:
strobe1(r2);
break;
case 2:
strobe2(r2);
break;
case 3:
strobe3(r2);
break;
case 4:
strobe4(r2);
break;
default:
darkness();
}
}
}
Thursday, November 1, 2018
Sunday, September 9, 2018
Robot Code
This is the operating code for a robot I built called Dumbot. It only has a motion sensor and moves randomly. The code generates three random numbers: speed, time, movement type. There are five different movement types: Forward, backward, turn right, turn left, and stop. There is a check routine at the beginning: Forward, right, backward, left. To check to make sure the motors are installed properly. This code was tested on a PIC16F1825, using hobby motors from Sparkfun and the brushed motor controller breakout board from Sparkfun. A switched battery holder with three double A batteries from Jameco was used. The wheels and frame were 3D printed. An LED output and an audio output were included.
/*
* File: R06Main.c
* Author: hmikelson
*
* Created on September 4, 2018, 6:11 PM
*/
#include <xc.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#pragma config MCLRE=OFF,CP=OFF,WDTE=OFF,FOSC=INTOSC
#define _XTAL_FREQ 16000000
unsigned char sPORTA, sPORTC, pwmax=31;
void init()
{
//Configure GPIO Port
TRISA = 0b110000000; //Set all Output
TRISC = 0b110001000; //Set up pin 3 for input
OSCCONbits.IRCF = 0b1111;
OSCCONbits.SCS = 0b00;
//OPTION_REG = 0b01111111; //Global enable weak pullups
//WPUC = 0b00001000; //Enable weak pullups with a 1
// Set up analog input
ANSELCbits.ANSC3 = 1;
ADCON0 = 0b00011101; //Channel (CHS4:0 bits 6-2),ADON bit 1 enable Analog
ADCON1bits.ADCS = 0b111; // clock select dedicated osc
ADCON1bits.ADNREF = 0; //neg ref
ADCON1bits.ADPREF = 0; //config + voltage with vdd
ADCON1bits.ADFM = 1; //format left justified
ADRESH = 0x00; //Init the AD Register
ADRESL = 0x00; // I don't think this is needed
//OSCCONbits.SPLLEN = 0b1;
}
void vdelay(int n)
{
int i;
for (i=0;i<=n;i++)
{
__delay_us(100);
}
}
int read_v()
// Read voltage from input
{
int val,v1,v2;
__delay_ms(1);
ADCON0bits.GO_nDONE = 1;
while(ADCON0bits.GO_nDONE == 1);
v1 = ADRESH;
v2 = ADRESL;
val = (v1<<8) + v2;
return val;
}
// Drive robot forward
void RobotFd(int time, unsigned char speed)
{
int i, j;
for (i=0;i<time;i++)
{
for (j=0;j<pwmax;j++)
{
if (j<speed)
{
PORTA = 0b00111110; //
PORTC = 0b00010110; // Enable on pin 4
vdelay(pwmax/speed);
}
else
{
PORTA = 0b00000110; // I think there is a clock output on pin 4 which I don't know how to disable
PORTC = 0b00010010; // Enable on pin 4
vdelay(pwmax/speed);
}
}
}
}
// Drive Robot backward
void RobotBk(int time, unsigned char speed)
{
int i, j;
for (i=0;i<time;i++)
{
for (j=0;j<pwmax;j++)
{
if (j<speed)
{
PORTA = 0b00111101;
PORTC = 0b00010101;
vdelay(pwmax/speed);
}
else
{
PORTA = 0b00000101;
PORTC = 0b00010001;
vdelay(pwmax/speed);
}
}
}
}
void RobotRt(int time, unsigned char speed)
{
int i, j;
for (i=0;i<time;i++)
{
for (j=0;j<pwmax;j++)
{
if (j<speed)
{
PORTA = 0b00111110;
PORTC = 0b00010101;
vdelay(pwmax/speed);
}
else
{
PORTA = 0b00000110;
PORTC = 0b00001001;
vdelay(pwmax/speed);
}
}
}
}
void RobotLt(int time, unsigned char speed)
{
int i, j;
for (i=0;i<time;i++)
{
for (j=0;j<pwmax;j++)
{
if (j<speed)
{
PORTA = 0b00111101;
PORTC = 0b00110110;
vdelay(pwmax/speed);
}
else
{
PORTA = 0b00000101;
PORTC = 0b00001010;
vdelay(pwmax/speed);
}
}
}
}
void RobotSt(int time)
{
int i;
for (i=0;i<time;i++)
{
PORTA = 0b00000100;
PORTC = 0b00001100;
__delay_ms(10);
}
}
void main()
{
int rmode, rtime, volts,mt=31;
unsigned char rspeed, nactions=0;
init();
RobotFd(100,pwmax/2);
RobotSt(1);
RobotRt(100,pwmax/2);
RobotSt(1);
RobotBk(100,pwmax/2);
RobotSt(1);
RobotLt(100,pwmax/2);
RobotSt(1);
while(1)
{
if (nactions > 0)
{
rmode=(rand() & 7) + 1;
nactions=nactions-1;
}
else
{
rmode = 0;
}
rtime = (rand() & 7)+1;
rspeed = rand() & pwmax;
switch (rmode)
{
case 1:
RobotFd(rtime*mt,rspeed);
RobotSt(1);
break;
case 2:
RobotBk(rtime*mt,rspeed);
RobotSt(1);
break;
case 3:
RobotRt(rtime*mt,rspeed);
RobotSt(1);
break;
case 4:
RobotLt(rtime*mt,rspeed);
RobotSt(1);
break;
case 0:
RobotSt(1);
volts = read_v();
if (volts>50)
{
nactions = 10;
//blink(volts);
}
break;
default:
RobotSt(10);
break;
}
}
}
Thursday, February 11, 2016
L-Systems in AutoLISP
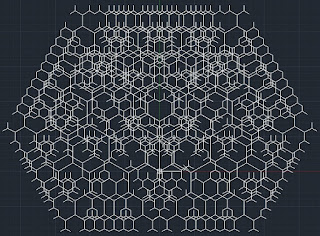
One of the beautiful things about AutoCAD is the AutoLISP language which comes with it. Experienced LISP programmers are likely to be familiar with the power of this early artificial intelligence language. It is particularly well suited to CAD applications. One of my favorite types of computer generated image is the L-System. These systems follow some basic rules and rely on recursive subroutine calls to generate complexity. Recursion is when a computer subroutine has the ability to call itself. Only a few of the early programming languages had this capability which is one reason that LISP was so powerful for its time.
The other thing that I find amazing is the amount of complexity that can be generated from relatively simple code. Following is the code used to generate this image. You may need to fix the line wraps. The radians to degrees and degrees to radians routines I got from the internet.
; converts radians to degrees
(defun RtD (r) (* 180.0 (/ r pi)))
; converts degrees to radians
(defun DtR (d) (* pi (/ d 180.0)))
(defun ls1 (x y alpha delta n) ; Sample Call: (ls1 0.0 0.0 90.0 25.0 7)
; x, y are the starting coordinates for the drawing
; Alpha is the starting angle, 90 means straight up
; Delta is the angle of each branch from the starting angle
; N is the number of iterations, it also controls the length of each branch
(cond ((> n 1) ; Check to see if n is small down to 1 yet
(setq x2 (+ x (* (cos (DtR alpha)) n))) ; Set up X2 and Y2 coordinates
(setq y2 (+ y (* (sin (DtR alpha)) n))) ; X2 = X + N * cos(alpha)
(setq p1 (list x y 0.0)) ; Create points 1 and 2
(setq p2 (list x2 y2 0.0))
(command "pline" p1 p2 "") ; Draw a line from X,Y to X2,Y2
(ls1 x2 y2 (+ alpha delta) delta (1- n)); Call the subroutine again
; Add alpha and delta, n-1
(ls1 (+ x (* (cos (DtR alpha)) n)) (+ y (* (sin (DtR alpha)) n)) (- alpha delta) delta (1- n)) ; Call again
)
(T) ; This is required to end the cond, it is always true
)
)
This is pretty simple code with hidden complexity. I think the X2 and Y2 are globals because they seemed to change values when I put them in as parameters to the subroutine. Save this code to your macro library and load it using "Load Application." You may need to allow AutoCAD to run macros. Turn OSNAP off by hitting F3. To get the image below run it with the sample run call:
(ls1 0.0 0.0 90.0 25.0 7)
Wednesday, December 2, 2015
AutoLISP Snowflakes
In this article I will describe a technique for making snowflakes similar to those that you may have learned to make as a child, where you fold a piece of paper up into thirds, then fold it in half, then cut out parts. With this procedure you can obtain a similar result using AutoCAD and then cut it out on a laser engraver.
- First of all you need to create a couple of lines at a 30 degree angle to each other. Select the LINE tool, type 0,0 of the starting point, then rotate up and type 10 on the Y axis or type in 0,10 to create a vertical line 10 units long.
- Rotate the line using the ROTATE command, select the line and hit enter, specify the origin as the point of rotation, hit C <enter> to copy and then 30 to rotate 30 degrees.
- If you are making a bunch of snowflakes you might want to make this shape into a block.
- I like to set up my OSNAP so that I can snap to Nearest.
- Use LINE, PLINE or other tools to make the "cuts" in the wedge. Remember if you are actually cutting on a laser engraver you will want your shape to remain intact.
- Delete the two straight lines.
- Use the (sf1) macro to make the snowflake. First save the AutoLisp code to snowflake.lsp. Click Manage, Load Application, Select the location with the file snowflake.lsp, type (sf1) at the command line. You may have to escape a couple of times to exit the command.
- If you don't want to use AutoLISP you can just mirror your lines around the 90 degree line, delete the line and then use polar array, repeat 6 to generate the snowflake.
;Snowflake generator
(defun sf1 ()
(setq p1 (list 0.0 0.0 0.0))
(setq p2 (list 0.0 10.0 0.0))
(command "mirror" "ALL" "" p1 p2 "N")
(command "ARRAYPOLAR" "ALL" "" p1 6 360.0 "" "")
)
Sunday, October 11, 2015
Laser Box AutoLISP Code
This code can be used to generate a laser box with dove-tail edges. It includes a kerf feature and should be used as in AutoCAD. You need to know how to use AutoLISP macros to use this.
Sorry this is fairly long and I didn't put in many comments so hopefully you can make sense of it. If not comment and I will explain further.
; Jig Saw Line X Outy
(defun jsbx1 (x1 x2 y1 n s krf)
(setq n2 (* n 2))
(setq dx (- x2 x1))
(setq px (* (/ dx (+ n2 1)) 2.0))
(setq tx (+ (/ px 2.0) krf))
(setq gx (- (/ px 2.0) krf))
(setq p1 (list x1 y1 0.0))
(repeat n
(list
(setq p2 (list (+ (car p1) tx) y1 0))
(setq p3 (list (+ (car p1) tx) (+ y1 s) 0))
(setq p4 (list (+ (car p2) gx) (+ y1 s) 0))
(setq p5 (list (+ (car p2) gx) y1 0))
(command "pline" p1 p2 p3 p4 p5 "")
(setq p1 p5)
))
(setq p2 (list (+ (car p1) tx) y1 0))
(command "pline" p1 p2 "")
)
; Jig Saw Line Y Outy
(defun jsby1 (x1 y1 y2 n s krf)
(setq n2 (* n 2))
(setq dy (- y2 y1))
(setq py (* (/ dy(+ n2 1)) 2.0))
(setq ty (+ (/ py 2.0) krf))
(setq gy (- (/ py 2.0) krf))
(setq p1 (list x1 y1 0.0))
(repeat n
(list
(setq p2 (list x1 (+ (cadr p1) ty) 0))
(setq p3 (list (+ x1 s) (+ (cadr p1) ty) 0))
(setq p4 (list (+ x1 s) (+ (cadr p2) gy) 0))
(setq p5 (list x1 (+ (cadr p2) gy) 0))
(command "pline" p1 p2 p3 p4 p5 "")
(setq p1 p5)
))
(setq p2 (list x1 (+ (cadr p1) ty) 0))
(command "pline" p1 p2 "")
)
; Jig Saw Line X Inny
(defun jsbx2 (x1 x2 y1 n s krf)
(setq n2 (* n 2))
(setq dx (- x2 x1))
(setq px (* (/ dx (+ n2 1)) 2.0))
(setq tx (+ (/ px 2.0) krf))
(setq gx (- (/ px 2.0) krf))
(setq p1 (list (+ x1 (abs s)) (+ y1 s) 0.0))
(setq p2 (list (+ x1 gx krf) (+ y1 s) 0.0))
(setq p3 (list (car p2) y1 0.0))
(command "pline" p1 p2 p3 "")
(setq p1 p3)
(repeat (- n 1)
(list
(setq p2 (list (+ (car p1) tx) y1 0))
(setq p3 (list (+ (car p1) tx) (+ y1 s) 0))
(setq p4 (list (+ (car p3) gx) (+ y1 s) 0))
(setq p5 (list (+ (car p3) gx) y1 0))
(command "pline" p1 p2 p3 p4 p5 "")
(setq p1 p5)
))
(setq p2 (list (+ (car p1) tx) y1 0))
(setq p3 (list (+ (car p1) tx) (+ y1 s) 0))
(setq p4 (list (- (+ (car p3) gx krf) (abs s)) (+ y1 s) 0))
(command "pline" p1 p2 p3 p4 "")
)
; Jig Saw Line Y Inny
(defun jsby2 (x1 y1 y2 n s krf)
(setq n2 (* n 2))
(setq dy (- y2 y1))
(setq py (* (/ dy(+ n2 1)) 2.0))
(setq ty (+ (/ py 2.0) krf))
(setq gy (- (/ py 2.0) krf))
(setq p1 (list (+ x1 s) (+ y1 (abs s)) 0.0))
(setq p2 (list (+ x1 s ) (+ y1 gy krf) 0.0))
(setq p3 (list x1 (cadr p2) 0.0))
(command "pline" p1 p2 p3 "")
(setq p1 p3)
(repeat (- n 1)
(list
(setq p2 (list x1 (+ (cadr p1) ty) 0))
(setq p3 (list (+ x1 s) (+ (cadr p1) ty) 0))
(setq p4 (list (+ x1 s) (+ (cadr p3) gy) 0))
(setq p5 (list x1 (+ (cadr p3) gy) 0))
(command "pline" p1 p2 p3 p4 p5 "")
(setq p1 p5)
))
(setq p2 (list x1 (+ (cadr p1) ty) 0))
(setq p3 (list (+ x1 s) (+ (cadr p1) ty) 0))
(setq p4 (list (+ x1 s) (- (+ (cadr p3) gy krf) (abs s)) 0))
(command "pline" p1 p2 p3 p4 "")
)
; Jig Saw Line X Mixed
(defun jsbx3 (x1 x2 y1 n s krf)
(setq n2 (* n 2))
(setq dx (- x2 x1))
(setq px (* (/ dx (+ n2 1)) 2.0))
(setq tx (+ (/ px 2.0) krf))
(setq gx (- (/ px 2.0) krf))
(setq p1 (list (+ x1 (abs s)) y1 0.0))
(setq p2 (list (- (+ (car p1) tx) (abs s)) y1 0.0))
(command "pline" p1 p2 "")
(setq p1 p2)
(repeat (- n 1)
(list
(setq p2 (list (car p1) (+ y1 s) 0))
(setq p3 (list (+ (car p1) gx) (+ y1 s) 0))
(setq p4 (list (+ (car p1) gx) y1 0))
(setq p5 (list (+ (car p3) tx) y1 0))
(command "pline" p1 p2 p3 p4 p5 "")
(setq p1 p5)
))
(setq p2 (list (car p1) (+ y1 s) 0))
(setq p3 (list (+ (car p1) gx) (+ y1 s) 0))
(setq p4 (list (+ (car p1) gx) y1 0))
(setq p5 (list (- (+ (car p3) tx) (abs s)) y1 0))
(command "pline" p1 p2 p3 p4 p5 "")
)
; Jig Saw Line Y Mixed
(defun jsby3 (x1 y1 y2 n s krf)
(setq n2 (* n 2))
(setq dy (- y2 y1))
(setq py (* (/ dy(+ n2 1)) 2.0))
(setq ty (+ (/ py 2.0) krf))
(setq gy (- (/ py 2.0) krf))
(setq p1 (list (+ x1 s) y1 0.0))
(setq p2 (list (car p1) (+ y1 gy krf) 0.0))
(command "pline" p1 p2 "")
(setq p1 p2)
(repeat (- n 1)
(list
(setq p2 (list x1 (cadr p1) 0))
(setq p3 (list x1 (+ (cadr p1) ty) 0))
(setq p4 (list (+ x1 s) (+ (cadr p1) ty) 0))
(setq p5 (list (+ x1 s) (+ (cadr p3) gy) 0))
(command "pline" p1 p2 p3 p4 p5 "")
(setq p1 p5)
))
(setq p2 (list x1 (cadr p1) 0))
(setq p3 (list x1 (+ (cadr p1) ty) 0))
(setq p4 (list (+ x1 s) (cadr p3) 0))
(setq p5 (list (+ x1 s) (+ (cadr p3) gy krf) 0))
(command "pline" p1 p2 p3 p4 p5 "")
)
;(jsb 4.0 6.0 5 0.11 0.01)
;Outy
(defun jsb1 (x1 x2 y1 y2 nx ny s krf)
(jsbx1 x1 x2 y1 nx s krf)
(jsby1 x1 y1 y2 ny s krf)
(jsbx1 x1 x2 (+ y2 krf) nx (- s) krf)
(jsby1 (+ x2 krf) y1 y2 ny (- s) krf)
)
;(jsb 4.0 6.0 5 0.11 0.01)
;Inny
(defun jsb2 (x1 x2 y1 y2 nx ny s krf)
(jsbx2 x1 x2 y1 nx s krf)
(jsby2 x1 y1 y2 ny s krf)
(jsbx2 x1 x2 (+ y2 krf) nx (- s) krf)
(jsby2 (+ x2 krf) y1 y2 ny (- s) krf)
)
;(jsb 4.0 6.0 5 0.11 0.01)
;Mixed
(defun jsb3 (x1 x2 y1 y2 nx ny s krf)
(jsbx3 x1 x2 y1 nx s krf)
(jsbx3 x1 x2 (+ y2 krf) nx (- s) krf)
(jsby3 x1 y1 y2 ny s krf)
(jsby3 (+ x2 krf) y1 y2 ny (- s) krf)
)
(defun jsb (x y z nx ny nz s krf)
(jsb1 0.0 x 0.0 y nx ny s krf)
(jsb1 (+ x 0.5 s) (+ x x 0.5 s) 0.0 y nx ny s krf)
(jsb2 (+ (* x 2) 1.0 s) (+ (* x 3) 1.0 s) 0.0 z nx nz s krf)
(jsb2 (+ (* x 3) 1.5 s) (+ (* x 4) 1.5 s) 0.0 z nx nz s krf)
(jsb3 (+ (* x 4) 2.0 s) (+ (* x 4) z 2.0 s) 0.0 y nz ny s krf)
(jsb3 (+ (* x 4) z 2.5 s) (+ (* x 4) z z 2.5 s) 0.0 y nz ny s krf)
)
The main routine is jsb. At the AutoCAD command line you would type:
(jsb 2.0 3.0 4.0 2 3 4 0.125 0.01)
to generate a box 2"x3"x4" with 2 tabs, 3 tabs, and 4 tabs respectively for 1/8" wood with a laser width (kerf) of 1/100th of an inch. Don't forget to turn off object snap (f3) (and other snaps). You should get something like the following:
Thursday, April 9, 2015
Half Normal Probability Paper
The code below can be used to generate half normal probability paper. The erfinv function is a bit inaccurate (2 sig figs) so it could be improved with a better approximation. Update: I modified this with the code from Wikipedia to give better accuracy. Create a blank file first. Mine was 1500 by 2000. The code is Python. I had to install Pillow for this.
from PIL import Image,ImageDraw,ImageFont
from math import *
def halfnormal(z,s):
return erf(z/sqrt(2)/s)
def erfinv(z):
a = .147
x=sqrt(sqrt((2/pi/a+log(1-z**2)/2)**2-log(1-z**2)/a)-(2/pi/a+log(1-z**2)/2))
#print z,z-erf(x)
return x
def invhalfnorm(z,s):
return erfinv(z)*sqrt(2)
def halfnormalgraph():
im = Image.open("blank_graph.png")
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(im)
font1 = ImageFont.truetype("arial.ttf", 16)
font2 = ImageFont.truetype("arial.ttf", 28)
j=30.0
k=700.0
xmax=46
xshift=30
gridfill = (180,180,250)
draw.text((550,10), "Half Normal Probability Paper", font=font2, fill=256)
for i in range(xmax):
x1=j*i+j*2+xshift
y1=im.size[1]-j*2
y2=j*2
draw.line((x1, y1, x1, y2), fill=gridfill)
x1=j*2+xshift
x2=j*xmax+j+xshift
for i in range(10):
iv=i/20.0+0
y1=im.size[1]-invhalfnorm(iv,1.0)*k-j*2
draw.line((x1, y1, x2, y1 ), fill=gridfill)
draw.text((2+xshift,y1-8), "{:10.0f}".format(iv*100), font=font1, fill=256)
for i in range(20):
iv=i/50.0+.5
y1=im.size[1]-invhalfnorm(iv,1.0)*k-j*2
draw.line((x1, y1, x2, y1 ), fill=gridfill)
draw.text((2+xshift,y1-8), "{:10.0f}".format(iv*100), font=font1, fill=256)
for i in range(10):
iv=i/100.0+.90
y1=im.size[1]-invhalfnorm(iv,1.0)*k-j*2
draw.line((x1, y1, x2, y1 ), fill=gridfill)
draw.text((2+xshift,y1-8), "{:10.0f}".format(iv*100), font=font1, fill=256)
im.save("halfnormgraph.png")
Here is another program that makes the desired number of divisions and an example of the output. This would be useful for plotting full factorial designed experiments, DOE, with 2 levels and 3 factors. Included are sheets for 7, 15, and 31 divisions which are the ones most useful for full factorial experiments.
def hng2(bins=7):
im = Image.open("blank_graph.png")
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(im)
font1 = ImageFont.truetype("arial.ttf", 16)
font2 = ImageFont.truetype("arial.ttf", 28)
j=30.0
k=700.0
xmax=46
xshift=30
gridfill = (180,180,250)
draw.text((550,10), "Half Normal Probability Paper", font=font2, fill=256)
for i in range(xmax):
x1=j*i+j*2+xshift
y1=im.size[1]-j*2
y2=j*2
draw.line((x1, y1, x1, y2), fill=gridfill)
x1=j*2+xshift
x2=j*xmax+j+xshift
iv=0.0
y1=im.size[1]-invhalfnorm(iv,1.0)*k-j*2
draw.line((x1, y1, x2, y1 ), fill=gridfill)
draw.text((-2+xshift,y1-8), "{:10.2f}".format(iv*100), font=font1, fill=256)
for i in range(bins):
iv=1.0*i/bins+1.0/2.0/bins
y1=im.size[1]-invhalfnorm(iv,1.0)*k-j*2
draw.line((x1, y1, x2, y1 ), fill=gridfill)
draw.text((-2+xshift,y1-8), "{:10.2f}".format(iv*100), font=font1, fill=256)
im.save("hng2.png")
hng2(7)
Friday, March 27, 2015
Spider Eyes
/*
* File: spider2main.c
* Author: hmikelson
*
* Created on March 24, 2015, 4:30 PM
*/
#if defined(__XC)
#include <xc.h> /* XC8 General Include File */
#elif defined(HI_TECH_C)
#include <htc.h> /* HiTech General Include File */
#endif
#include <stdint.h> /* For uint8_t definition */
#include <stdbool.h> /* For true/false definition */
#include <stdlib.h> /*rand()*/
#pragma config MCLRE=OFF,CP=OFF,WDTE=OFF,FOSC=INTOSCIO
#define _XTAL_FREQ 4000000
uint8_t sGPIO;
void init()
{
//Configure GPIO Port
ANSEL = 0b00000000; //Configure all GPIO pins as digital
TRISIO = 0b11001000; //Set GP3 as input and the rest as outputs
OPTION_REGbits.nGPPU = 0;
WPU = 0b00000100; //Enable weak pullups on GP2
//Configuer AD Convertor
ADCON0 = 0x00; //AD disabled
ADRESH = 0x00; //Init the AD Register
//Configure Comparator
CMCON0 = 0xFF; // Comparator is turned off
CMCON1 = 0x00; // Comparator is turned off
//Interrupt configuration
INTCON = 0x00; //Disable all interrupts
}
void vdelay(int n)
{
int i;
for (i=0;i<=n;i++)
{
__delay_us(1);
}
}
void fade_eyes(int n) // PWM sweep high f to low f
{
int i;
{
for (i=0;i<n;i++)
{
GPIO = 0b11000101;
vdelay(i);
GPIO = 0b11000000;
vdelay(n-i);
}
for (i=0;i<n;i++)
{
GPIO = 0b11000101;
vdelay(n-i);
GPIO = 0b11000000;
vdelay(i);
}
}
}
void scan_eyes(int n) // PWM sweep high f to low f
{
int i,j,k;
int i1,i2,i3,pw1,pw2;
uint8_t sGPIO;
i1=1; i2=-1; pw1=0; pw2=n;
sGPIO = GPIO;
for (k=0;k<6;k++)
{
for (j=0;j<n;j++)
{
for (i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if (i>pw1)
{
sGPIO = sGPIO & 0b11111110;
}
else
{
sGPIO = sGPIO | 0b00000001;
}
if (i>pw2)
{
sGPIO = sGPIO & 0b11111011;
}
else
{
sGPIO = sGPIO | 0b00000100;
}
GPIO = sGPIO;
}
pw1 = pw1 + i1;
pw2 = pw2 + i2;
}
i3 = i1; i1 = i2, i2 = i3;
}
}
void dark_eyes(void) // PWM sweep high f to low f
{
GPIO = 0b11000000;
__delay_ms(1000);
}
void main()
{
uint8_t r,r2;
init();
while(1)
{
r=rand()%8;
r2 = rand()%8+1;
//r=3;
switch (r)
{
case 1:
fade_eyes(100*r2);
break;
case 2:
fade_eyes(20*r2);
break;
case 3:
scan_eyes(20*r2);
break;
default:
dark_eyes();
}
}
}
* File: spider2main.c
* Author: hmikelson
*
* Created on March 24, 2015, 4:30 PM
*/
#if defined(__XC)
#include <xc.h> /* XC8 General Include File */
#elif defined(HI_TECH_C)
#include <htc.h> /* HiTech General Include File */
#endif
#include <stdint.h> /* For uint8_t definition */
#include <stdbool.h> /* For true/false definition */
#include <stdlib.h> /*rand()*/
#pragma config MCLRE=OFF,CP=OFF,WDTE=OFF,FOSC=INTOSCIO
#define _XTAL_FREQ 4000000
uint8_t sGPIO;
void init()
{
//Configure GPIO Port
ANSEL = 0b00000000; //Configure all GPIO pins as digital
TRISIO = 0b11001000; //Set GP3 as input and the rest as outputs
OPTION_REGbits.nGPPU = 0;
WPU = 0b00000100; //Enable weak pullups on GP2
//Configuer AD Convertor
ADCON0 = 0x00; //AD disabled
ADRESH = 0x00; //Init the AD Register
//Configure Comparator
CMCON0 = 0xFF; // Comparator is turned off
CMCON1 = 0x00; // Comparator is turned off
//Interrupt configuration
INTCON = 0x00; //Disable all interrupts
}
void vdelay(int n)
{
int i;
for (i=0;i<=n;i++)
{
__delay_us(1);
}
}
void fade_eyes(int n) // PWM sweep high f to low f
{
int i;
{
for (i=0;i<n;i++)
{
GPIO = 0b11000101;
vdelay(i);
GPIO = 0b11000000;
vdelay(n-i);
}
for (i=0;i<n;i++)
{
GPIO = 0b11000101;
vdelay(n-i);
GPIO = 0b11000000;
vdelay(i);
}
}
}
void scan_eyes(int n) // PWM sweep high f to low f
{
int i,j,k;
int i1,i2,i3,pw1,pw2;
uint8_t sGPIO;
i1=1; i2=-1; pw1=0; pw2=n;
sGPIO = GPIO;
for (k=0;k<6;k++)
{
for (j=0;j<n;j++)
{
for (i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if (i>pw1)
{
sGPIO = sGPIO & 0b11111110;
}
else
{
sGPIO = sGPIO | 0b00000001;
}
if (i>pw2)
{
sGPIO = sGPIO & 0b11111011;
}
else
{
sGPIO = sGPIO | 0b00000100;
}
GPIO = sGPIO;
}
pw1 = pw1 + i1;
pw2 = pw2 + i2;
}
i3 = i1; i1 = i2, i2 = i3;
}
}
void dark_eyes(void) // PWM sweep high f to low f
{
GPIO = 0b11000000;
__delay_ms(1000);
}
void main()
{
uint8_t r,r2;
init();
while(1)
{
r=rand()%8;
r2 = rand()%8+1;
//r=3;
switch (r)
{
case 1:
fade_eyes(100*r2);
break;
case 2:
fade_eyes(20*r2);
break;
case 3:
scan_eyes(20*r2);
break;
default:
dark_eyes();
}
}
}
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)